
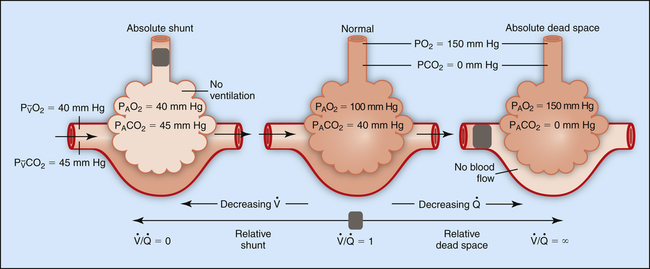
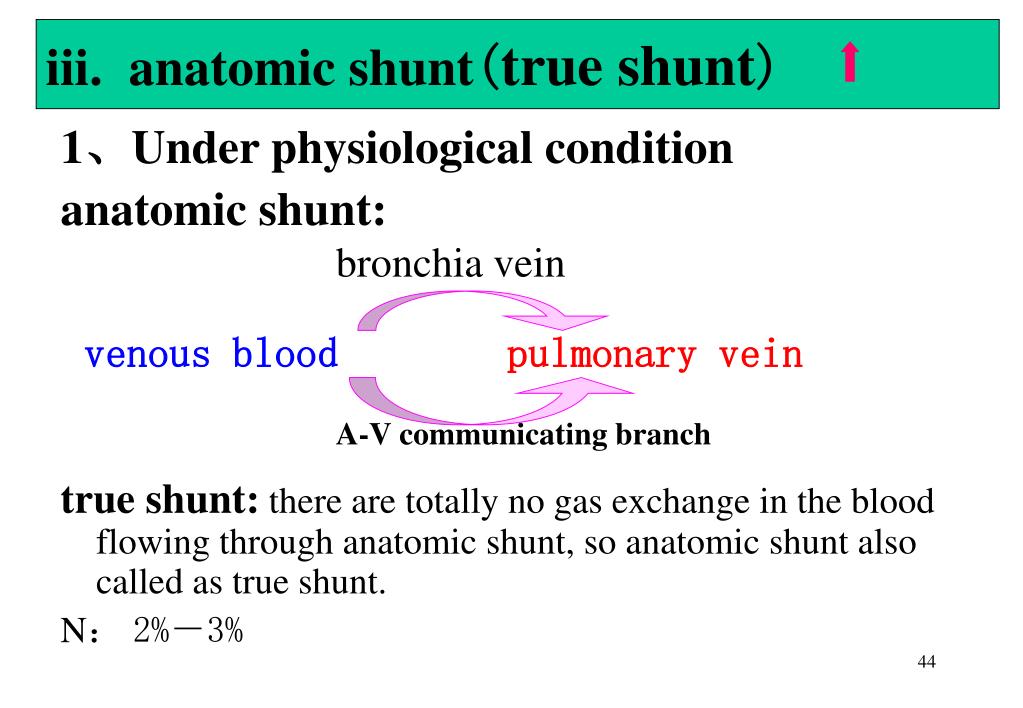
Some apparatus dead space may actually reduce total dead space, as an ETT bypasses the majority of anatomical dead space of the patient (nasopharynx).ĭead space from the patient. For example, a 30 shunt (from pneumonia) with no alveolar deadspace produces an AaPO 2 of almost 50 torr, but an aAPCO2 of only 3 torr. Types of Dead Spaceĭead space from equipment, such as tubes ventilator circuitry. Dead space: the physiology of wasted ventilation An elevated physiological dead space, calculated from measurements of arterial CO2 and mixed expired CO2, has proven to be a useful clinical marker of prognosis both for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and for patients with severe heart failure. olar-arterial PO2 and PCO2 differences (AaPO2, aAPCO2) are converted to corresponding physiological shunt and deadspace val-ues using the Riley and Cournand 3-compartment model. Glomerular Filtration and Tubular Functionĭead space is the proportion of minute ventilation which does not participate in gas exchange. Functional Anatomy and Control of Blood Flow


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
